WHAT IS CANNABIDIVARIC ACID (CBDVA)?
Like other cannibinoids, cannabidivarinic acid (CBDVA) is found in Cannabis sativa and is the precursor of cannabidivarin (CBDV). The ‘A’ indicates that this compound is an acidic form of cannabidivarin.
Only a fraction of information is known of when, and how, cannabidivarinic acid (CBDVA) was identified, but insights can be drawn from when its precursor (CBDV) was first identified. Although first isolated in 1969, CBDV was probably first reported in a benzene extract from a Thai Cannabis variety referred to as “Meao”.
Hindered Research on Cannabinoids
Up until 2018, research on cannabinoids was hamstrung by the DEA Controlled Substances Act, and certified reference materials are severely lacking because of this. Prior to the Farm Bill of 2018, CBDVA was on this list of controlled substances, which made research incredibly difficult to conduct.
The Farm Bill removed hemp, and hemp derived compounds from this list so long as they contained less than 0.3% THC. This is why research is only now beginning for many of these cannabinoids.
Very little is known of CBDVA. Just like the CBDV, it has received little attention and is short of certified reference material. That said, it is expected to become a more interesting area of research in the near future. Despite this, it is evident that cannabidivarinic acid (CDBVA) possesses properties and potential benefits.
HOW CBDVA WORKS
For those who don’t already know, cannabinoids are derived from plants in the Cannabis genus, mostly hemp and marijuana.
Cannabinoids interact with the available CB1 and CB2 receptors in the human body, which are part of the human endocannabinoid system. This system helps regulate many different things for us.
The prefix “endo” at the beginning of the word indicates that it is produced from within the body. Basically, endocannabinoids are a form of cannabinoids produced by the human body to help regulate systems that control pain, appetite and neurological function, cognitive function, motor strength, and moods.
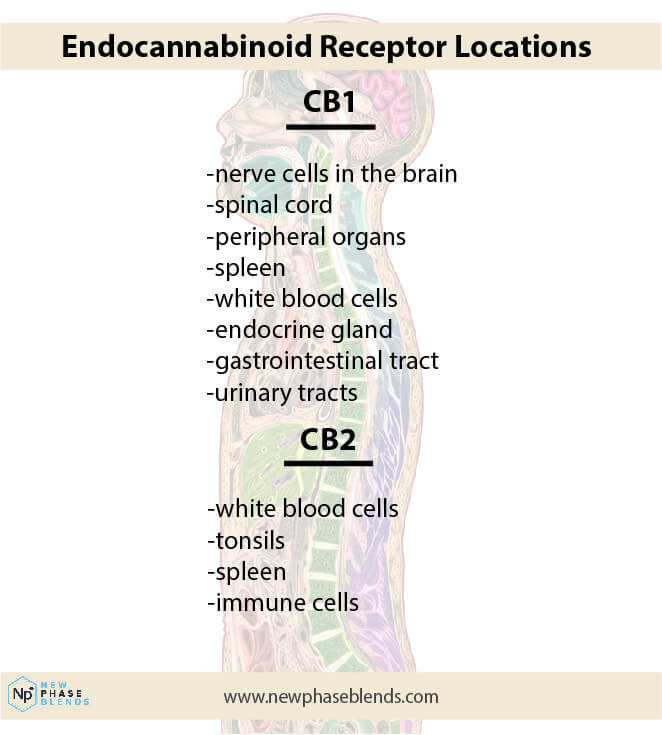
There’s a lot more to this bodily system.
Studies on CBDVA
In a study on the effects of cannabidiolic acids in a mouse model of Dravet Syndrome, it was recorded that “rapid absorption of CBDVA was observed following intraperitoneal administration with a plasma tmax of 15 min and a t1/2 of 49 min. Absorption into the brain was slightly delayed, as the tmax was 30 min; however, the Cmax was quite low and elimination was rapid (t1/2 19 min) (Anderson, et al.).”
At 60 min after consumption, CBDVA was detected in the brain tissue, but was below the limit of quantification (LOQ), so a value of 1/2 LOQ (0.25 ng/mg brain) was used. Elimination was complete by 90 min.
The brain−plasma ratio (0.02) suggests CBDVA exhibits poor brain penetration.
The neutral form of CBDVA, CBDV, was not detected in the brain or plasma following injection of CBDVA, suggesting there is no significant decarboxylation of CBDVA to CBDV in vivo following i.p. injection.
These tests were all done with isolate forms of these compounds. When researchers use prepared stock, this can eliminates many variables which could skew data.
This certified reference material suggests that cannabidivarinic acid has the potential to serve as a anticonvulsant against hyperthermia induced seizures.
CBDVA testing methods must be precise, and in house standards preparation of these compounds should reflect this.
Potential Therapeutic Benefits
Although little is known of CBDVA, this is not an indication that it has no therapeutic benefits. It is a cannabinoid, and many different cannabinoids are known for easing anxiety, slow tumor growth, reducing symptoms of nausea and vomiting, stimulating appetites, relaxing the body, and reducing seizure activity.
That said, CBDVA has a capacity for anti-inflammatory benefits that can ease arthritis pain, swelling from an injury, and constant pain from chronic conditions. These effects are demonstrated via certified reference material that you can find in the reference section of this article.
Having anti-inflammatory properties means it is capable of remedying pain by reducing inflammation. Many people in the United States use opioids to reduce levels of moderate to severe pain. While opioids work well at reducing pain, they come with a slew of adverse side effects.
CBDVA works completely differently than opioids, which affect the central nervous system by blocking pain signs to the brain. This implies cannabidivarinic acid (CBDVA) can work as an analgesic to reduce pain and inflammation, without the harsh side effects.
INTERESTING FACTS
CBDVA has no capacity to induce a “high” when used. Only quality products can be used this way. High quality, prepared stock product guarantees this.

References
Lyndsey L. Anderson, Ivan K. Low, Samuel D. Banister, and Jonathon C. Arnold, “Pharmacokinetics of Phytocannabinoid Acids and Anticonvulsant Effect of Cannabidiolic Acid in a Mouse Model of Dravet Syndrome” Journal of Natural Products.
Shoyama, Y., Hirano, H., Makino, H., Umekita, N., Nishioka, I., 1977. Cannabis. X. The isolation and structures of four new propyl cannabinoid acids, tetrahydrocannabivarinic acid, cannabidivarinic acid, cannabichromevarinic acid and cannabigerovarinic acid, from Thai cannabis, Meao variant. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 25 (9), 2306–2311.
Vollner L, Bieniek D, Korte F. 1969. Hashish. XX. Cannabidivarin, a new hashish constituent. Tetrahedron Letters 3:145–147 DOI 10.1016/S0040-4039(01)87494-3. Amada et al. (2013), PeerJ, DOI 10.7717/peerj.2141
Stone NL, Murphy AJ, England TJ, O’Sullivan SE. A systematic review of minor phytocannabinoids with promising neuroprotective potential. Br J Pharmacol. 2020;177(19):4330-4352. doi:10.1111/bph.15185
Gulk, T., Moller, B. Phytocannabinoids: Origin and Biosynthesis. Feature Review. 2020; 25(10):985-1004. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2020.05.005
















