WHAT IS CANNABIDIOLIC ACID (CBDA)?
With the consistent drive by researchers to discover more about Cannabidiol (CBD), and other cannabinoids that exist within the cannabis plant, new compounds are being discovered. Each one contains its unique properties and potential medicinal uses. One of these discovered cannabinoids is Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA).
CBDA is one of several other acidic cannabinoids produced by cannabis plants that’s recently been discovered by scientists.
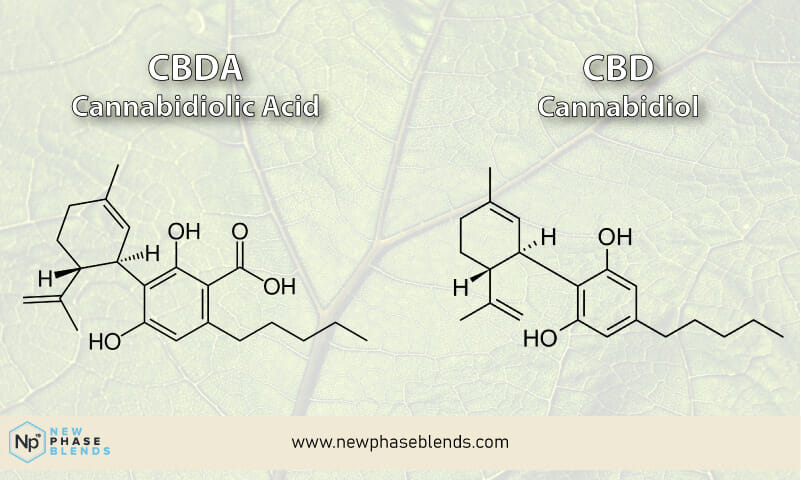
It is a derivative of CBD.
Related article: The Differences Between CBDA and CBD
Remember, both hemp and marijuana make up the cannabis plant family.
CBDA was first recognized in 2008 via a study that was done by the American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Journal (ASPET). It was discovered by ASPET that CBDA is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid, unlike its other counterpart THC. It was also discovered that CBDA has the same anti-inflammatory benefits as CBD.
Since its’ discovery, a series of studies have been ongoing to create a concrete foundation of understanding the cannabis plant and the cannabinoids within the cannabis plant.
Some of these studies report that the compound shows huge potential in treating inflammation, anxiety, aches, and also in improving mood.
Discover: CBD Gummies for Anxiety
A recent study conducted by Orgeon State University concluded that CBDA, and CBGA (another acidic cannabis compound) may actually prevent the spread of the COVID 19 virus in human cells.
Unfortunately, a lot of these studies are done with major cannabinoids like CBD, THC, or even CBN. Their derivatives lack comprehensive studies, so it makes it very difficult to give concrete evidence in regards to their therapeutic effects or uses.
Creating the Cannabinoid Known As CBDA
While the first compound that is formed in the plant is CBDA, when heated, it loses its acidic carboxyl group and then converts to CBD – the process whereby the acidic carboxyl group is lost is known as decarboxylation.
More simply put, CBDA is converted to CBD when exposed to forms of heat. This is how major cannabinoid precursor compounds are converted into compounds that will bind to endocannabinoid receptors.
Related: CBD vs CBN
This heating process can occur either naturally when the plant is left to slowly degrade over time, or with the intervention of humans when the cannabis plant is smoked or exposed to other methods of extreme heat.
How Does CBDA Affect The Body?
We have what are known as CB receptors in our brain that are made to bind directly with psychoactive cannabinoids that are found in cannabis plants, like THC. These receptors make up what is known as the endocannabinoid system.
CBDA does not work in the same way as THC does with this bodily system.
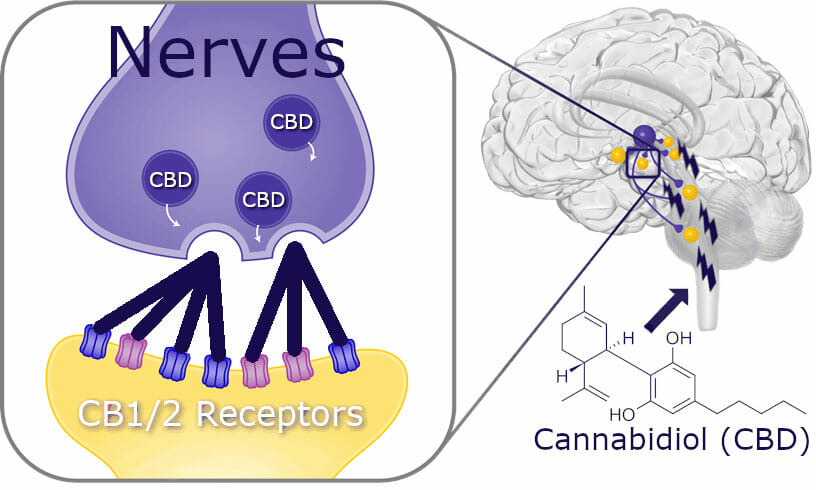
THC has a very strong binding affinity for CB receptors, which is why it products the high effect that so many people have heard of. CBDA interacts with the endocannabinoid system by inhibiting the Cox-2 enzyme, which does not directly affect the central nervous system.
CBD, and derivatives of CBD, are thought to bind very weakly to their receptor locations. There are even some scientists who believe CBD binds with other receptors that have not been discovered yet.
POSSIBLE THERAPEUTIC BENEFITS
Interestingly enough, CBDA may have a stronger activation of 5-HT1A receptors for seratonin, when compared to its’ parent molecule CBD. Serotonin regulates many different things for us, including our moods, feelings of nausea, vomiting, and intestinal regulation.
Even though potential CBDA benefits have been shown in numerous therapeutic studies, it is yet to be an acceptable clinical means of treatment. Being an unstable compound, research is still going on to see how it can be stable, and how it can become a viable option for clinical use.
Here are some of the therapeutic benefits of CBDA:
Prevention of COVID 19 Virus
Oregon State University released a ground breaking study in January of 2022.
In a study headed by Richard van Breemen, findings specify that CBDA (in addition to CBGA) can prevent the virus that in responsible for COVID-19 from entering human cells.
For Nausea and vomiting
In a study that was done on mice and rats, it was reported that CBDA was able to reduce anticipatory nausea and vomiting. It was said to be more potent at controlling nausea than CBD. Raw cannabis juice works well here.
For Depression and anxiety
There is a serious discussion surrounding the ability of CBD to reduce anxiety. Likewise, studies were done using rats to determine the effectiveness of CBDA against anxiety and depression. It was recorded that rats pre-treated with CBDA did not exhibit any form of anxiety in response to the test carried out on them.
Discover: Using CBD for Stress
For Breast Cancer
A 2012 study showed that CBDA was able to stop the migration and invasion of deadly human breast cancer cells. Another study also showed that CBDA was able to suppress genes that are associated with breast cancer.
INTERESTING FACTS
- CBDA acid becomes CBD. It is then heated in a process called decarboxylation to form CBD. The conversion of THCA to THC works the same way.
- It has been shown by scientists that CBDA has 100 times the binding affinity for certain receptors when compared to CBD from raw cannabis.

REFERENCES
Citti C, Pacchetti B, Vandelli MA, Forni F, Cannazza G. Analysis of cannabinoids in commercial hemp seed oil and decarboxylation kinetics studies of cannabidiolic acid (CBDA). J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Feb 5;149:532-540. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2017.11.044. Epub 2017 Nov 20. PMID: 29182999.
Bolognini, D., Rock, E., Cluny, N., Cascio, M., Limebeer, C., Duncan, M., … Pertwee, R. (2013). Cannabidiolic acid prevents vomiting inSuncus murinusand nausea-induced behaviour in rats by enhancing 5-HT1Areceptor activation. British Journal of Pharmacology, 168(6), 1456–1470.
Rock EM, Limebeer CL, Petrie GN, Williams LA, Mechoulam R, Parker LA. Effect of prior foot shock stress and delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiolic acid, and cannabidiol on anxiety-like responding in the light-dark emergence test in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017;234(14):2207-2217. doi:10.1007/s00213-017-4626-5
Takeda, S., Okajima, S., Miyoshi, H., Yoshida, K., Okamoto, Y., Okada, T., … Aramaki, H. (2012). Cannabidiolic acid, a major cannabinoid in fiber-type cannabis, is an inhibitor of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell migration. Toxicology Letters, 214(3), 314–319.
Parker LA, Rock EM, Limebeer CL. Regulation of nausea and vomiting by cannabinoids. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;163(7):1411-1422. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01176.x
Van Breemen RB, Muchiri RN, Bates TA, Weinstein JB, Leier HC, Farley S, Tafesse FG. Cannabinoids Block Cellular Entry of SARS-CoV-2 and the Emerging Variants. J Nat Prod. 2022 Jan 10. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.1c00946. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35007072.
Back to List of Cannabinoids















