Have you ever wondered if CBD products might trigger the munchies like its cousin THC? You’re not alone. As CBD products gain popularity for their potential wellness benefits, many people question how this cannabis compound might affect their appetite. Whether you’re considering CBD for therapeutic purposes or simply curious about its effects, understanding the relationship between CBD and hunger is essential for informed decision-making.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the science behind CBD’s impact on appetite, separate fact from fiction, and provide practical insights for those interested in incorporating CBD into their wellness routine. Drawing from current research and clinical observations, we’ll answer your most pressing questions about CBD and hunger.
The Relationship Between CBD and Appetite
Unlike THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), the psychoactive component in cannabis that famously triggers “the munchies,” CBD (cannabidiol) interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system differently. This fundamental difference explains why CBD’s effects on appetite may be more subtle and complex.
How CBD Works in the Body
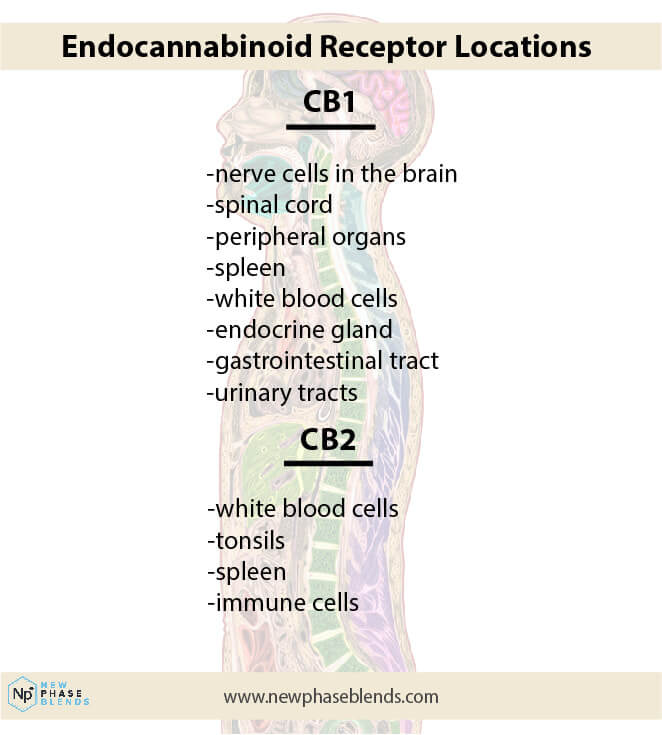
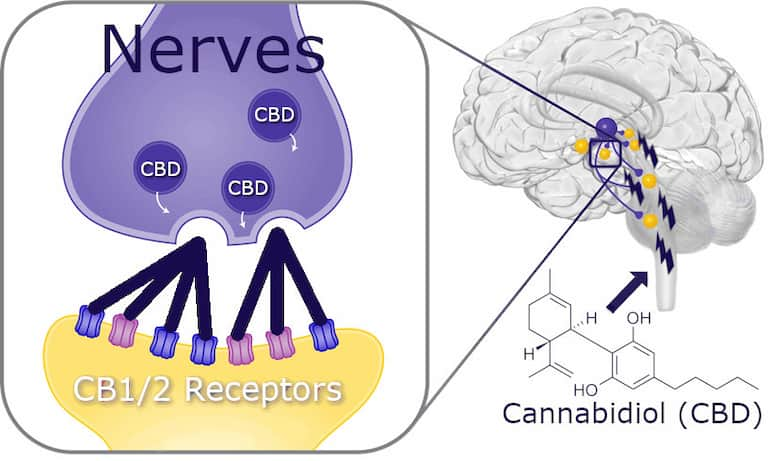
CBD interacts with the endocannabinoid system (ECS), a complex network of receptors throughout the body that helps regulate numerous physiological processes, including appetite and metabolism. However, unlike THC, which directly binds to CB1 receptors to stimulate hunger, CBD works indirectly.
CBD primarily influences the body through multiple pathways. It interacts indirectly with CB1 and CB2 receptors while also affecting serotonin receptors, vanilloid receptors, and other neurotransmitter systems throughout the body. These complex interactions create a cascade of effects that can influence hunger and metabolism in various ways, often dependent on the individual’s unique physiology and current state of health.
What Research Shows About CBD and Hunger
Current scientific evidence presents a nuanced picture of CBD’s relationship with appetite. Research from the British Journal of Pharmacology suggests that CBD may actually reduce appetite in some cases, contrary to the common assumption that all cannabis products increase hunger. This finding challenges the stereotype that CBD functions like THC in this regard.
A 2012 study published in Psychopharmacology found that CBD did not significantly affect food intake in healthy participants, indicating that it may be neutral on appetite for many people. However, research published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation shows that CBD can potentially increase appetite indirectly by reducing symptoms that may suppress hunger, such as nausea, anxiety, and pain.
Does CBD Increase Appetite? The Truth Behind the Question
The answer to whether CBD increases appetite isn’t straightforward because CBD’s effects vary based on several factors.
Individual Factors That Influence CBD’s Effect on Hunger
A person’s baseline health condition significantly impacts how CBD affects their appetite. People using CBD to address conditions that affect appetite (like anxiety or chronic pain) may experience different outcomes than healthy individuals. Additionally, dosage and product type matter—different CBD formulations and dosages may produce varying effects on appetite. Full-spectrum products containing trace amounts of THC might have different effects than CBD isolate.
Each person’s endocannabinoid system responds uniquely to cannabinoids, creating personalized responses to CBD. Furthermore, individual metabolic rates and body chemistry can significantly influence how CBD affects appetite. These factors combine to create highly individualized responses to CBD that can’t be universally predicted.
Common Scenarios Where CBD Might Affect Appetite
For individuals with conditions that suppress appetite, CBD may help restore normal hunger signals by reducing anxiety that causes loss of appetite, alleviating nausea that prevents eating, decreasing pain that interferes with enjoyment of food, and improving mood, which can enhance appetite. Cancer patients experiencing treatment-related appetite loss sometimes report improved hunger when using CBD as a complementary therapy. Similarly, those with anxiety-related appetite suppression might find that CBD’s calming effects help normalize their eating patterns.
In some cases, CBD might actually reduce hunger by potentially boosting metabolism, interacting with receptors that regulate satiety, and reducing inflammation that can trigger excessive hunger. People using CBD for weight management occasionally report feeling less driven by cravings and emotional eating, though these effects are not universal or guaranteed.
The Science of CBD’s Impact on Metabolism
Beyond direct effects on hunger, CBD may influence appetite through its impact on metabolism. Research in the journal Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry suggests that CBD may influence fat browning—the process of converting white adipose tissue (fat that stores energy) into brown adipose tissue (fat that burns energy). This process could potentially increase calorie burning and affect appetite regulation.
CBD might also influence insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, which play crucial roles in hunger signals. A 2016 study published in Diabetes Care found that CBD might have potential in improving certain metabolic parameters, though more research is needed.
CBD vs. THC: Understanding the Difference in Appetite Effects
It’s important to distinguish between CBD and THC when discussing cannabis and hunger. THC directly stimulates appetite by binding to CB1 receptors in the brain, enhancing the pleasure of eating by increasing dopamine release, heightening sensory perception of food, and stimulating hunger hormones.

CBD, on the other hand, does not directly bind to CB1 receptors in the same way. It may actually modulate or reduce THC’s appetite-stimulating effects while working through multiple indirect pathways. The effects of CBD vary significantly between individuals, making it less predictable than THC in terms of appetite impact.
Practical Considerations for CBD Users
If you’re considering using CBD and are concerned about potential appetite effects, consider these practical guidelines for minimizing unwanted changes to your hunger patterns.
How to Use CBD Without Unwanted Appetite Changes
Start with low doses and gradually increase to find your optimal amount. This methodical approach allows you to monitor any appetite changes and adjust accordingly. Tracking your hunger patterns when beginning CBD helps you notice any changes that might be related to your CBD use.
Consider the timing of your CBD consumption—some users report different effects depending on whether they take CBD with meals or between them. If you’re concerned about THC’s appetite-stimulating effects, choose CBD isolate products to avoid even trace amounts of THC that might be present in full-spectrum products.
Before starting any CBD regimen, especially if you have existing appetite or metabolic concerns, consult with a healthcare provider familiar with cannabinoids. Their expertise can help you navigate potential effects based on your specific health situation.
CBD Product Selection Tips
When selecting CBD products with appetite effects in mind, consider that full-spectrum products contain trace amounts of THC and other cannabinoids that may produce different appetite effects than isolated CBD. CBD isolate products contain only CBD and no THC, potentially reducing any hunger-stimulating effects.
CBD Products for Sale by New Phase Blends
Type: CBD oil for energy
CBD: 16mg per serving
Features: Synephrine and CBD blend for energy & focus enhancement
Type: CBD Acne Cream
CBD: 1000mg per 1oz jar
Features: Salicylic acid and CBD blend to stop acne
Type: High strength CBD balm
CBD: 1000mg or 2000mg
Features: Free shipping, money back guarantee
Type: CBD Starter Kit Bundle
Includes: Tincture, Balm, and Gummies
Features: You create your own kit with your custom product choices
Type: Pure CBD Softgel Capsules (Vegan)
CBD: 40mg per Capsule
Features: Free Shipping, Money Back Guarantee
Type: CBD gummies for sleep
CBD: 45mg per gummy
Features: Free Shipping, Money Back Guarantee
Type: CBD Oil For Sleep
CBD: 66mg per serving
Features: Free shipping, money back guarantee
The product format matters significantly—oils and tinctures absorbed sublingually may produce different systemic effects than topical products, which typically don’t significantly affect appetite. Quality is also crucial; third-party tested products from reputable manufacturers are more likely to produce consistent effects and provide accurate information about cannabinoid content.
Common Misconceptions About CBD and Hunger
Several misconceptions exist regarding CBD and appetite that deserve clarification. One common myth suggests that “CBD always gives you the munchies.” This misconception stems from confusing CBD with THC. As discussed earlier, CBD does not typically produce the intense hunger known as “the munchies” that THC is famous for. In fact, some research suggests CBD might counteract THC’s appetite-stimulating properties.
Another widespread belief is that “CBD is an effective weight loss supplement.” While some preliminary research suggests CBD might influence metabolism in ways that could theoretically support weight management, marketing CBD as a weight loss solution oversimplifies its complex effects. CBD is not approved for weight loss, and its effects on appetite and metabolism vary significantly between individuals.
Some also believe that “CBD has no effect on appetite.” This oversimplification ignores the complex ways CBD might indirectly influence hunger, particularly by addressing conditions like anxiety or pain that affect appetite. While CBD doesn’t directly stimulate hunger like THC, its effects on appetite cannot be universally described as neutral.
Expert Tips for Managing CBD’s Effects on Appetite
If you’re using CBD and concerned about potential appetite changes, consider keeping a journal tracking your CBD usage, dosage, timing, and any noticed changes in hunger or eating patterns. This personal data can help you identify patterns specific to your body’s response.
Experiment with different formats and dosages under appropriate guidance to find what works best for your body and goals. Consider the entourage effect—how CBD works in combination with other cannabinoids and terpenes might influence its effects on appetite.
Be aware of other factors like stress, sleep quality, and activity levels that might interact with CBD’s effects on hunger. These lifestyle elements can sometimes magnify or diminish CBD’s impact on appetite. Before using CBD for appetite-related concerns, consult healthcare providers knowledgeable about cannabinoids who can provide personalized guidance.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions About CBD and Appetite
The question “Does CBD make you hungry?” has no one-size-fits-all answer. CBD’s effects on appetite appear to be highly individualized, influenced by personal physiology, existing health conditions, product formulation, and dosage.
What we do know is that CBD does not typically stimulate appetite in the direct, intense way that THC does. For many users, CBD’s effects on hunger may be subtle or nonexistent. For others, particularly those using CBD to address conditions that affect appetite, the indirect benefits might include normalized eating patterns.
As research continues to evolve, our understanding of CBD’s complex relationship with appetite and metabolism will become clearer. In the meantime, approaching CBD with realistic expectations, starting with low doses, and monitoring your individual response remains the most prudent approach.
Whether you’re exploring CBD for wellness benefits or specific therapeutic purposes, being informed about its potential effects—including those on appetite—empowers you to make choices aligned with your personal health goals.


















