Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabiorcolic acid (THCA-C1) is the acidic form of THC-C1 and a derivative of CBN and CBGV. We have no specific information on this compound apart from its chemical structure and a few potential benefits when consumed.
There is quite a lack of scientific data on THCA-C1, and rightfully so.
What is Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabiorcolic Acid (THCA-C1)?
Related: What is Delta 9?
The hemp plant has health-enhancing compounds that researchers have been trying to uncover. THCA-C1 is one of the results after the 1940 discovery of the partial structure of cannabinol (CBN) was reported by the British chemist Robert S. Cahn. For decades, scientists have been looking into these compounds’ potential roles and effects of the cannabis plant.
Cannabinoids
THCA-C1 is found in combination with other compounds identified during these studies, such as CBD, CBC, CBG, CBN, and other compounds. Although research in these areas has been relatively sparse worldwide, it is worth knowing that the expeditions and discoveries so far have been extremely beneficial.
THCA-C1 is similar to other cannabinoids in its formation. Also, similar chemical reactions are observed, which in certain cases are de-carbonization and oxidation. The mother compounds of the cannabis plant all undergo processes leading to CBN and its derivatives.
Details on how THCA-C1 components assemble to become a body still need to be studied. However, we recognize that THCA-C1 is an acidic form of THC-C1, which means that the compound has extra oxygen and carbon.
Related read: Delta 8 THC vs CBD
The future of THCA-C1 is yet unknown. The knowledge and functions of its structure are lagging due to the creeping development in research of the plant. The legal tussle surrounding the legalization and use of hemp in most countries is a substantial hurdle to research.
On the surface, we know how much man benefits from the compounds found in the cannabis sativa plant. In addition to the toxic effects of hemp, research has shown that it can also be used to treat both disease or pain.
Related: How Long Does Delta 8 THC Stay In Your System?
How Does THCA-C1 Work Within Us?
While there is currently no study demonstrating how THCA-C1 functions, due to its similarities with the THC-C1, THC, and CBN, we can only guess that they act the same way with few discrepancies in function.
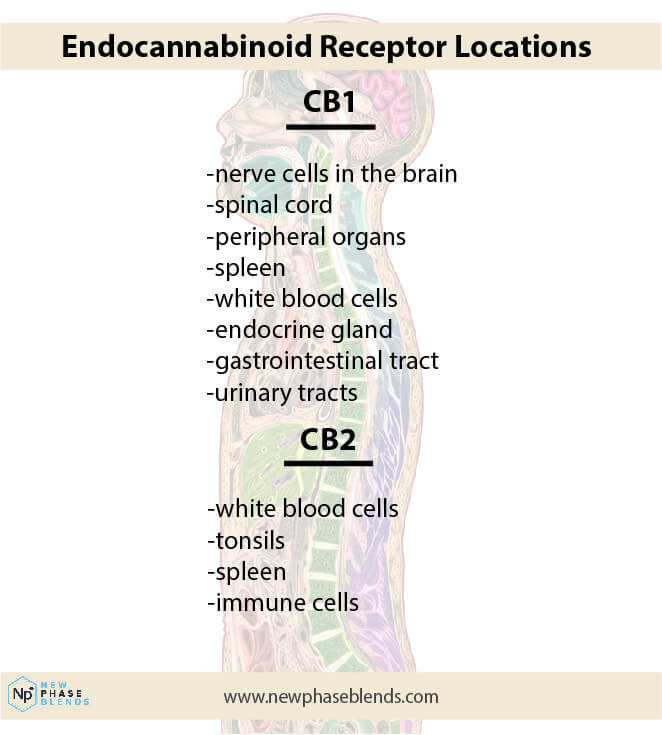
In medicine, we need studies, clinical testing, trials, and testing to prove how compounds truly operate. Speculations are fine, but never enough. Via the bindings in brains and nervous systems where they are located, THC acts with cannabinoid receptors in your body. THC lasts in the body longer than most other medications remaining just a few hours.
Possible Benefits of THCA-C1
The NCI notes related synthetic behavior between delta-9-THC and delta-8-THC, which has the common name dronabinol. In the fields of analgesics and appetite enhancement, they are claimed to be anti-nausea.
There may be discrepancies here, though, since there no clinical trial to prove this. There are some anecdotal reports that delta-8-THC is safer than delta-9-THC, but only clinical trials can confirm this.
A clinical trial to investigate dronabinol’s effect on the dosage of opiates prescribed in patients with breast cancer is currently in progress.
Interesting Facts
- Its molecular formula is C18H22O4.
- Its IUPAC name is (6ar,10ar)-1-hydroxy-3,6,6,9-tetramethyl-6a,7,8,10a-tetrahydro-6h-benzo[c]chromene-4-carboxylic acid.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 16078, Dronabinol. Andre, Christelle
M.; Hausman, Jean-Francois; Guerriero, Gea (2016-02-04). “Cannabis sativa: The Plant of the Thousand and One Molecules”.
Frontiers in Plant Science. 7: 19.doi:10.3389/fpls.2016.00019. ISSN1664-462X. PMC4740396. PMID26870049.
Back to List of Cannabinoids