Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabiorcol (THC-C1) is a non-electrophilic delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol derivative that stems from the CBN and CBGV compounds. Aside from its chemical structure and some expected abilities, we have no specific information on this compound.
As with other strange derivatives of THC, there is little-to-no peer reviewed data on THC-C1. That said, we’ll explore what we do know.
WHAT IS Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabiorcol (THC-C1)?
The cannabis plant generally has compounds that are beneficial to human health. THC-C1 is one of the discoveries since 1940 when British chemist Robert Cahn reported the partial structure of cannabinol (CBN).
Some researchers have since then, over decades, been looking into the cannabis plant for its functions and benefits. THC-C1 was discovered alongside other compounds of CBD, CBC, CBG, CBN discovered during that research.
Related: CBD vs CBN
THC-C1 is a derivative. Its formation is similar to that of other cannabinoids, and it goes through the same chemical reactions – de-carbonification and oxidization in some cases or as applied in various cases.
Related: THCA-C1
The mother compounds of the cannabis plant both undergo a process that leads to CBN and, eventually, its derivatives. Information on how the components of THC-C1 come together to become a body is still yet to be revealed.
Owing to the chemical configuration and location of its power cells, THC-C1 is of relevance. There is still plenty to look at in the cannabis plant. THC-C1 and other cannabinoids are not well understood right now, but a futuristic outlook is required. In addition to its psychoactive and medicinal properties, researchers are looking to expose other roles of the cannabis plants.
They expect that THC-C1 will be one of the main compounds to help advance medicine.
Related: What is Delta 9?
How Does THC-C1 Work In Our Bodies?
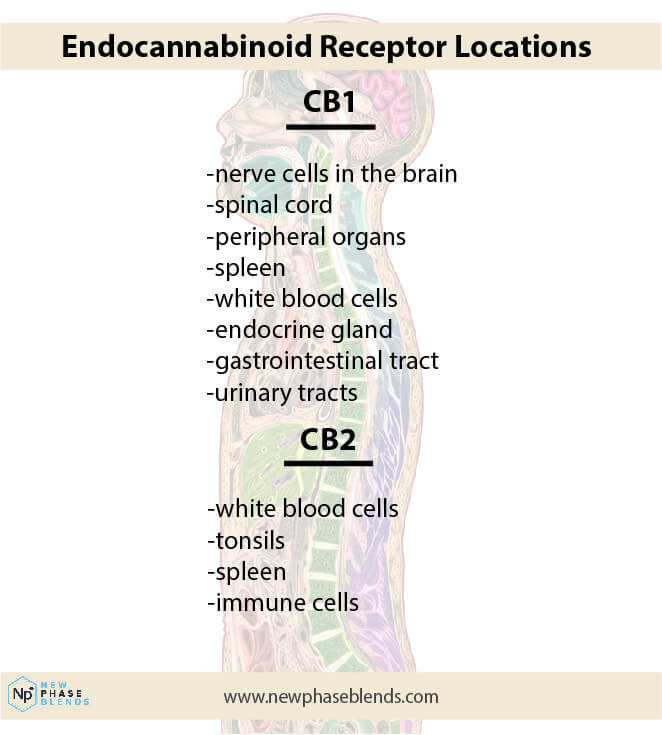
THC works with cannabinoid receptors in the body by binding with them in the brain and nervous system where they are found. THC stays longer in the body than most other drug substances, which only last for a few hours.
Related: How Long Does Delta 8 THC Stay In Your System?
THC-C1 is expected to work the same way, seeing that it is an antinociceptive compound. We expect it to bind with receptors in the human body as well. Although there is currently no research to prove this, we can only speculate and assume owing to its similarity to THC and CBN. Speculations are good but never enough in the world of science and medicine.
We need concrete research, clinical trials, experiments, and tests to ascertain exactly how THC-C1 works.
Are There Any Benefits of THC-C1?
THC-C1 is a non-electrophilic delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol derivative that is being studied for use as a pharmacological strategy for treating pain. Its other therapeutic benefits are also still being looked into.
Related: Benefits of CBD
Although, as at the time of writing, there is no conclusive evidence to show that THC-C1 can treat pain, THC-C1 has been confirmed to be an antinociceptive. This is the mechanism by which sensory nerves inhibit the perception of painful or dangerous stimuli.
Intraspinal narcotic antinociception requires a longer duration relative to systemic narcotic analgesia.
Interesting Facts
- It has a molar mass of 258.35 g/mol.
- Its molecular structure is C17H22O2.
- THC-C1 is similar to dronabinol, dexanabinol, cannabichromene, and synhexyl in chemical structure.
References
PubChem [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US), National Center for Biotechnology Information; 2004-. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 22805649, delta1-Tetrahydrocannabiorcol.
Andersson et al. TRPA1 mediates spinal antinociception induced by acetaminophen and the cannabinoid Delta9-tetrahydrocannabiorcol. Nature Communications, doi: 10.1038/ncomms.1559, published online 22 November 2011
Back to List of Cannabinoids