What is Delta 9 Tetrahydrocannabolic Acid (D9THCA)?
Even if you don’t know much about cannabis, there is a good chance you might have heard about Tetrahydrocannabinol, or simply THC.
THC also is known as delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, which is the compound in the cannabis plant that is responsible for its intoxicating effects. The abundance of the THC cannabinoid depends, largely, on the strain of cannabis grown, and certain extraction methods performed.
Certain strains of cannabis are bred and cultivated solely to get higher levels of THC, which make the plant effects more potent. However, THCA is a bit different in this regard.
Did you know you won’t get high off just eating a raw cannabis plant, no matter how potent the strain is?
That’s right. It’s true. This is because there is no THC in a raw, unprocessed cannabis plant.
What is present in the raw cannabis plant? Well, delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), of course. Do not confuse THC and THCA, because they are not the same.
More on THCA
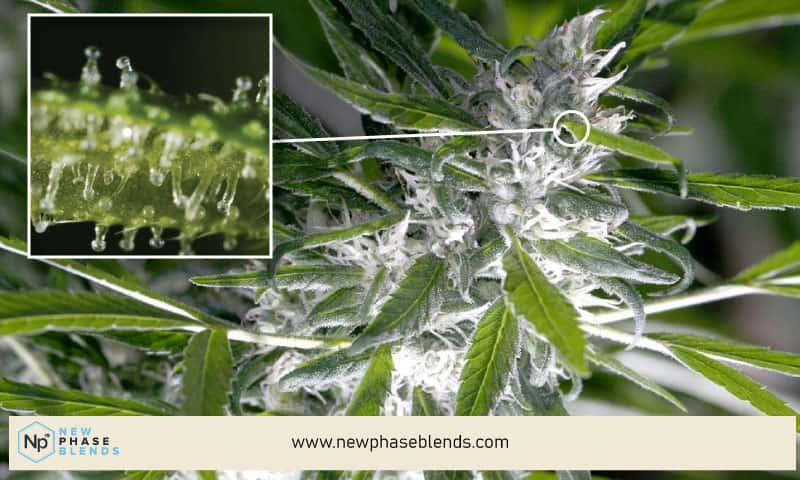
THCA is a cannabinoid that, until recently, has always been confused with THC. THCA-a was first identified by Professor Friedhelm Korte at the Univerity of Bonn in 1965. THCA is a non-psychoactive compound that is found in the fresh leaves and flowers (buds) of the cannabis plant.
This is the reason why eating raw cannabis leaves won’t get you high.
The feelings of being stoned, or high, can be felt once the raw cannabis plant is dried and heated. This process is known as decarboxylation.
THCA is converted to THC once the plant is exposed to heat, THCA loses its acidic carbonyl to become THC. When you cure cannabis, the THCA converts to the psychoactive form THC. This is why there is always a period of time involved that dries out the plant after it is harvested.
There is a reason people don’t just pluck off the buds and immediately smoke them. This is exactly why.
THCA is the non-psychoactive form of THC that is found in the cannabis plant. Many clinical studies have shown the potential of THCA in treating epilepsy, chronic pain, and many other ailments.
There is a reduced study because of the legalization issue facing the cannabis plant.
How Does Delta 9 THCA Work in Our Bodies?
Due to the extra acid group of THCA, the molecule does not attach to CB1 cannabinoid receptors, as THC does.
This is why THCA doesn’t give a psychoactive effect. THCA, however, attaches to the TRPM8 receptor (the one that makes us experience a sensation of cold when we taste mint) and activates the TRPA1 receptor (which makes us feel the spiciness when we eat things like mustard or cinnamon).
The therapeutic effect of THCA may be caused by its blocking MAGL enzymes. This type of enzyme is responsible for breaking down the cannabinoids produced by the body, which binds to CB1- and CB2 receptors.
Related: CBD vs THC
Unfortunately, not a lot of research has been done on this cannabinoid, making it unclear how THCA works. That said, we do know that it can help people in certain ways.
Are There Therapeutic Effects of Delta 9 THCA?
The limited research done concerning THCA makes people believe that the compound offers various medicinal benefits as it is said to be commonly used as a nutritional supplement and dietary enhancement aid.
Here are some of the therapeutic benefits that THCA may end up providing:
- Anti-inflammatory properties
- Certain forms of pain relief
- Managing seizures
- Neuroprotectant (nervous system protectant) properties
Note that these are yet to be proven medically as trials have only been done on lab rats. More research and human trials need to be done to make these claims.
Is THCA Healthy?
THCA isn’t necessarily a form of a health food, or anything like that. It is healthy from the perspective that it can help with some of the health benefits listed above. There has been a recent movement of people eating raw cannabis, in an effort to load themselves with high amounts of THCA.
Some people add it to foods and beverages, while other just eat it like a salad. More research is warranted on using THCA in this manner.
Other Interesting Facts
- THCA converts to the psychoactive form THC through the decarboxylation process.
- Eating raw marijuana plants will not get you high, because they contain high amounts of THCA – not THC. It takes a curing process to convert the THCA into THC.
References
De Petrocellis L, Ligresti A, Schiano Moriello A, et al. Non-THC cannabinoids inhibit prostate carcinoma growth in vitro and in vivo: pro-apoptotic effects and underlying mechanisms. Br J Pharmacol. 2013;168(1):79-102. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02027.x
E M Rock, R L Kopstick, C L Limebeer, L A Parker. Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid reduces nausea-induced conditioned gaping in rats and vomiting in Suncus murinus. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.12316
Nadal X, Del Río C, Casano S, Palomares B, Ferreiro-Vera C, Navarrete C, Sánchez-Carnerero C, Cantarero I, Bellido ML, Meyer S, Morello G, Appendino G, Muñoz E. Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid is a potent PPARγ agonist with neuroprotective activity. Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Dec;174(23):4263-4276. doi: 10.1111/bph.14019. Epub 2017 Nov 2. PMID: 28853159; PMCID: PMC5731255
Back to List of Cannabinoids