Have you ever wondered why certain activities like exercise or eating chocolate make you feel good? The answer might lie in a fascinating molecule called anandamide, often nicknamed the “bliss molecule.” In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what anandamide is, how it works in your body, and why it’s crucial for your well-being.
What is Anandamide?
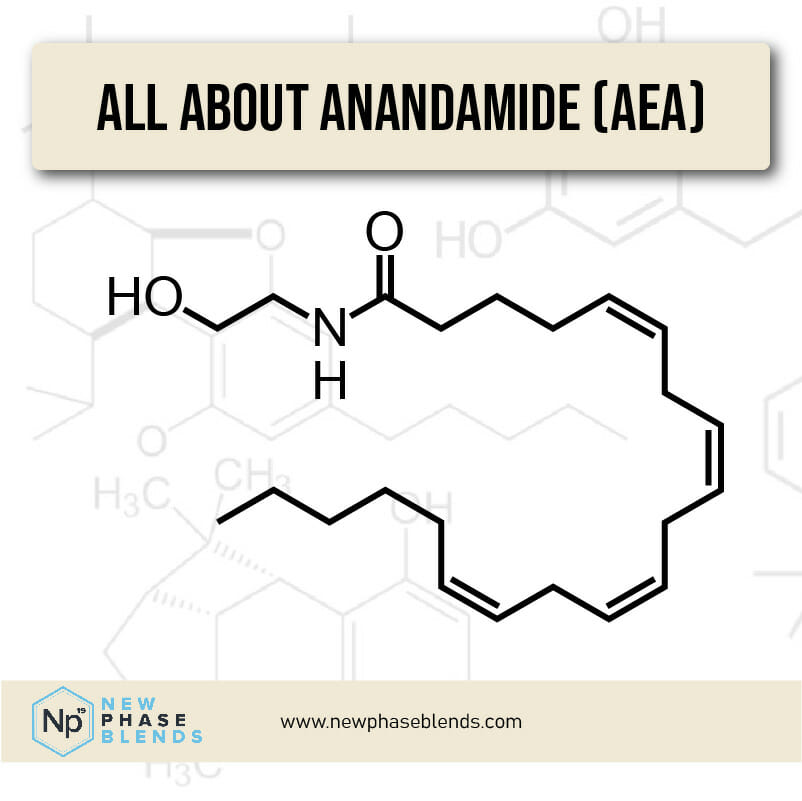
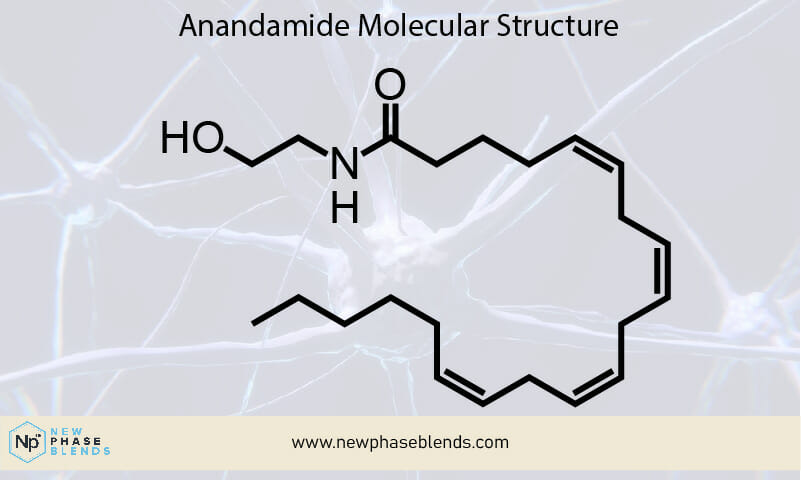
Anandamide (AEA) is a naturally occurring compound in your body that plays a vital role in maintaining mental and physical health. The name itself comes from the Sanskrit word “ananda,” meaning bliss or happiness, which hints at its important role in mood regulation.
As a neurotransmitter, anandamide belongs to a class of compounds called endocannabinoids – molecules produced by your body that are similar to the compounds found in cannabis plants. However, unlike cannabis-derived compounds, anandamide is produced naturally within your body and is essential for various biological functions.
The Science Behind Anandamide
Now that we understand how anandamide works within your body’s endocannabinoid system, let’s explore the fascinating scientific discoveries about its specific benefits. Researchers have uncovered compelling evidence about how this molecule influences various aspects of your physical and mental well-being.
Think of anandamide as a master regulator in your body – like a conductor coordinating different sections of an orchestra. When this conductor is working effectively, all the different systems in your body perform in harmony. Here’s what scientific research has revealed about anandamide’s key roles:
Memory and Learning
Anandamide plays a crucial role in how your brain forms and stores memories. It helps regulate the strength of connections between nerve cells, influencing both short-term and long-term memory formation.
Pain Management
When you experience pain, anandamide naturally increases in the affected areas, helping to reduce pain signals. This natural pain-management system demonstrates why maintaining healthy anandamide levels is important for overall comfort.
Mood Regulation
Scientists have found that appropriate anandamide levels are crucial for maintaining emotional balance. The molecule’s interaction with CB1 receptors influences serotonin levels, which affects your overall mood and sense of well-being.
CBD and Anandamide
CBD (Cannabidiol) has been shown to influence anandamide levels by slowing down its breakdown in the body. This interaction helps explain why many people report positive effects from CBD use, though it’s important to consult with healthcare providers before starting any new supplement regimen.
How Anandamide Works in the Human Body
Your body has an intricate system called the endocannabinoid system (ECS), which helps maintain balance across various bodily functions. Here’s how anandamide operates within this system:
Production: Your body creates anandamide from arachidonic acid, a type of fatty acid found in cell membranes.
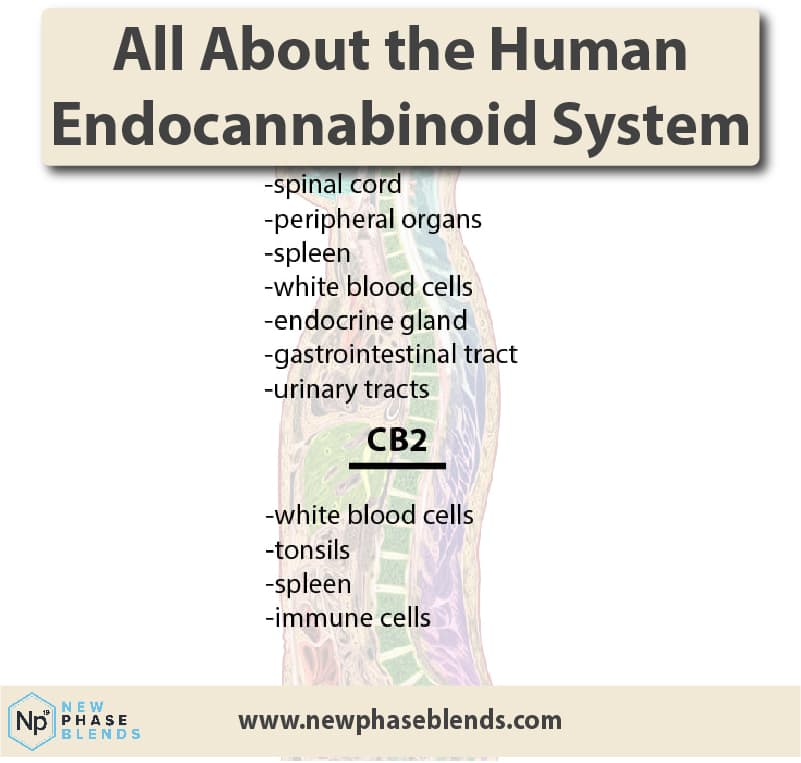
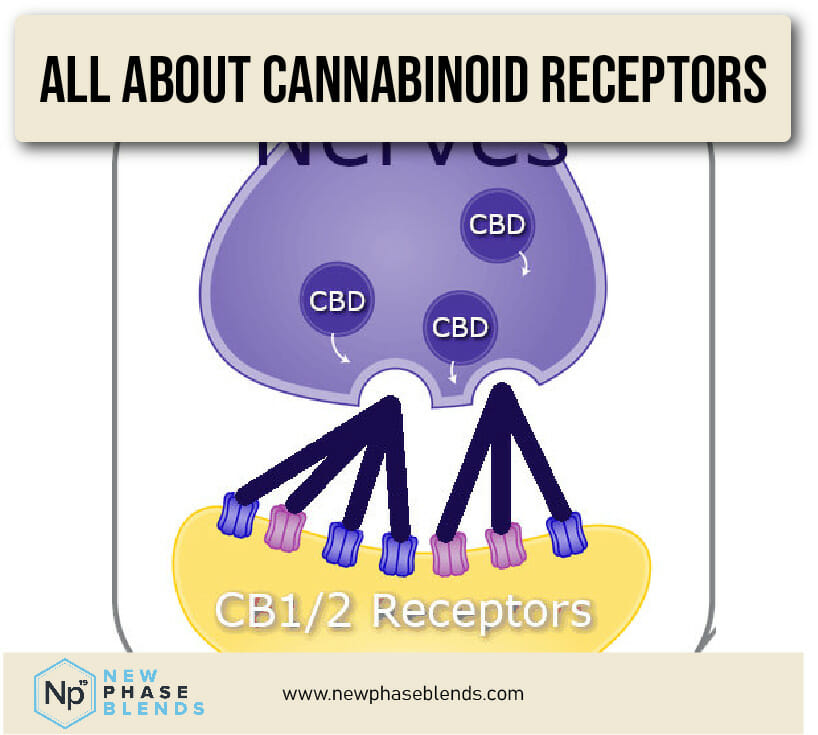
Receptor Interaction: Once produced, anandamide primarily binds to CB1 receptors, which are concentrated in:
- Your brain and central nervous system
- The peripheral nervous system
- Various organs throughout your body
Effects: Through these interactions, anandamide influences:
- Mood regulation
- Pain perception
- Memory formation
- Appetite control
- Stress response
Endocannabinoid System (ECS) Briefly Explained
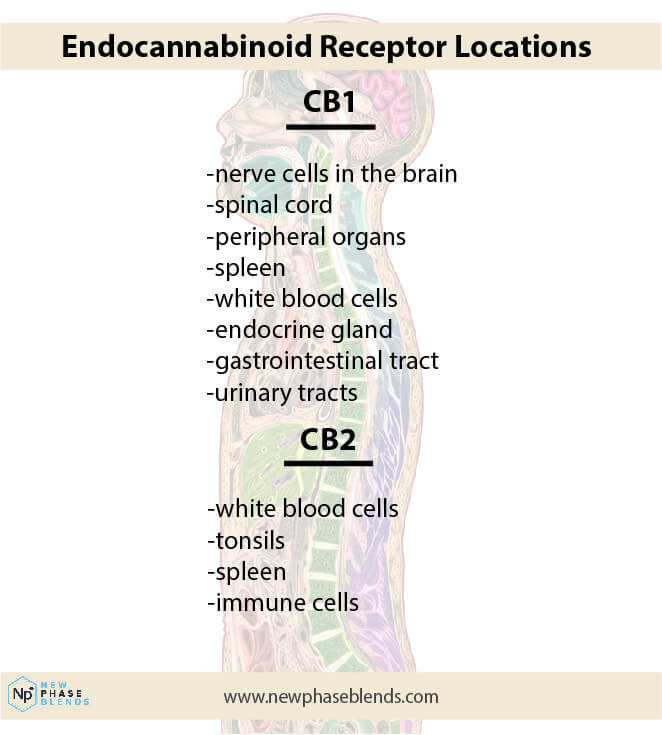
Anandamide binds to cannabinoid receptors that are known as ‘CB1’. Both the CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptor network make up a large network of cells known as the endocannabinoid system.
As you can see in the picture above, there are cannabinoid receptors all over the place. That said, a large potion of them remain in the central nervous system and brain stem.
For those who aren’t already aware, the ECS is a bodily system that is responsible for many different things, but maintaining a bodily homeostasis seems to be this system’s top priority. This system can use both endogenous cannabinoids and phytocannabinoids (like CBD) to accomplish different tasks.
Natural Ways to Increase Anandamide
Your daily choices can significantly impact how well your body produces and maintains anandamide levels. Let’s explore evidence-based approaches to optimize your body’s natural “bliss molecule” production:
Exercise and Physical Activity
Physical activity is one of the most powerful ways to boost anandamide levels naturally. Here’s how different types of exercise affect your anandamide system:
Aerobic Exercise: Running, swimming, and cycling for 30+ minutes trigger significant anandamide release. The famous “runner’s high” is partially attributed to increased anandamide production Moderate-intensity cardio (65-75% of max heart rate) appears optimal for anandamide production
Strength Training: Resistance exercises help maintain healthy endocannabinoid system function. Combined with aerobic activity, it provides complementary benefits for anandamide regulation. Post-workout recovery periods show elevated anandamide levels.
Dietary Approaches
Your food choices can significantly influence anandamide levels and function:
- Omega-3 fatty acids (found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts)
- Zinc (pumpkin seeds, oysters, grass-fed beef)
- Magnesium (dark leafy greens, almonds, avocados)
- B-vitamins (whole grains, legumes, nutritional yeast)
Specific Foods That Support Anandamide
Dark Chocolate (70% cocoa or higher):
- Dark chocolate contains compounds that slow anandamide breakdown. This provides precursor molecules for anandamide production.
- Recommended serving of dark chocolate: 1-2 squares daily (about 20-30g)
Truffles and Black Pepper:
- These items contain natural compounds that interact with endocannabinoid receptors. They can enhance anandamide’s effects in the body
Black Tea and Green Tea:
- Contain catechins that support overall endocannabinoid system health
- Provide antioxidants that protect anandamide-producing cells
Stress Management and Mental Well-being
Since stress can deplete anandamide levels, incorporating stress-reduction practices is crucial:
Meditation and Mindfulness: Daily meditation (10-20 minutes) helps maintain balanced anandamide levels. Mindful breathing exercises support endocannabinoid system function. Regular practice can improve long-term stress resilience
Sleep Optimization: Maintain consistent sleep schedule (7-9 hours nightly). Create a dark, cool sleeping environment. Limit blue light exposure before bedtime. Practice relaxation techniques before sleep.
Social Connection: Positive social interactions boost anandamide production. Regular social engagement supports overall endocannabinoid system health. Group activities combining social interaction and exercise provide synergistic benefits.
Environmental Factors
Your environment can influence anandamide function:
Sunlight Exposure: Morning sunlight exposure helps regulate endocannabinoid rhythms. Aim for 10-30 minutes of natural light daily. Consider light therapy during darker months.
Temperature Exposure: Cold exposure (like cold showers or winter sports) can boost anandamide production. Heat exposure (sauna sessions) may enhance endocannabinoid system function. Alternating between hot and cold shows promising benefits.
Supplementary Support
While whole foods should be your primary focus, certain supplements may support anandamide function:
- Turmeric/Curcumin: Supports overall endocannabinoid system health
- Probiotics: Maintain gut health, which influences endocannabinoid function
- Fish Oil: Provides essential fatty acids for optimal system function
- Lion’s Mane Mushroom: Supports neural health and endocannabinoid signaling
Note: Always consult with healthcare providers before starting any new supplement regimen.
Is anandamide a drug?
No, it is not a drug. It’s a chemical that is made from within our bodies via arachidonic acid in the long chain essential fats. In fact, the cb1 and cb2 receptors can actually be stimulated by endocannabinoids, like anandamide, in a way that makes drug withdrawals more manageable.
Where is anandamide found in the brain?
Anandamide, and other endocannabinoids, are actually released by neurons, then undergo diffusion into astrocytes and neurons, where they are broken down by a fatty acid amide hydrolase, or FAAH.
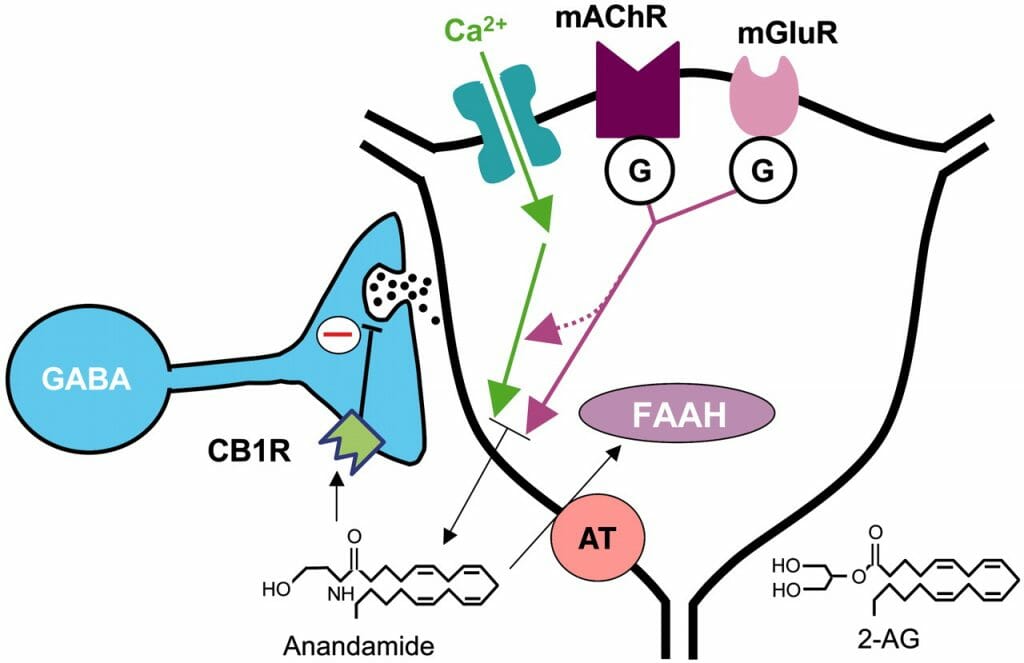
Fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH)
Fatty acid amide hydrolase is an enzyme that is specific to mammals. It aids in breaking down the fatty acid amide family of lipids. These lipids include anandamide, among other things.
Your body carefully regulates anandamide levels through an enzyme called Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH). This enzyme breaks down anandamide when levels get too high, helping maintain proper balance. Research suggests that variations in FAAH activity might explain why some people naturally have higher or lower anandamide levels.
Future Medical Applications of Anandamide
Current research into anandamide’s functions is opening new possibilities for medical treatments:
- Mental health conditions
- Pain management
- Inflammatory conditions
- Neurological disorders
Scientists are particularly interested in developing treatments that can influence anandamide levels or activity as a potentially safer alternative to current medications.
Summary – Anandamide May Be Part of the Future of Healthcare
It seems that some cannabinoid drugs which, right now, are under clinical trials for the treatment of some psychiatric disorders just may be the future for treatments when it comes to psychiatric disorders.
Since cannabinoids and endocannabinoids both target the same cb receptors (CB1 and CB2), they are both under constant scrutiny for what they can, and cannot do. Cannabinoids from cannabis sativa are not a replacement for anandamide, they just interact in a similar manner with our bodies as anandamide does.
The pharmacological effects and psychoactive effects of anandamide are still being studied by the scientific community. It will take more time, and more peer reviewed research, before the medical community can figure out how best to use endocannabinoids, like anandamide (AEA) or 2-archidonoyl glyerol (2-AG).
Leweke FM, Piomelli D, Pahlisch F, Muhl D, Gerth CW, Hoyer C, Klosterkötter J, Hellmich M, Koethe D. Cannabidiol enhances anandamide signaling and alleviates psychotic symptoms of schizophrenia. Transl Psychiatry. 2012 Mar 20;2(3):e94. doi: 10.1038/tp.2012.15. PMID: 22832859; PMCID: PMC3316151.
Maccarrone, M. Metabolism of the endocannabinoid anandamide: Open questions after 25 years. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 166.
Scherma M, Masia P, Satta V, Fratta W, Fadda P, Tanda G. Brain activity of anandamide: a rewarding bliss? Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019 Mar;40(3):309-323. doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0075-x. Epub 2018 Jul 26. PMID: 30050084; PMCID: PMC6460372.
*FDA disclaimer: none of the statements on this webpage have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration. These statements have not been evaluated by the FDA. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Medical advice should be sought before starting any supplement. If you are pregnant or nursing consult with a doctor. Medical advice should be sought if you have any pre-existing medical conditions. If you take other prescription medications, a doctor’s advice should be sought. Site void where prohibited.