CBD is a non-psychoactive compound found in the cannabis plant that has shown promise in treating various ailments. People even report using CBD for ulcerative colitis symptoms, successfully. CBD works by interacting with the endocannabinoid system in the body, which helps to regulate things like appetite, inflammation, and pain. A growing body of evidence suggests that CBD oil for ulcerative colitis may be an effective treatment for reducing inflammation and relieving pain and other symptoms.
TL;DR – Ulcerative colitis is something that cannot be cured by CBD, but CBD may be able to help manage some of the pain and discomfort that go along with it.
What is CBD?
CBD, also known as cannabidiol, is a plant chemical that occurs naturally in the hemp plant and marijuana plant. Both of these make up the cannabis plant family.
While they are both in the same family, hemp-derived CBD cannot get you high, while marijuana-derived CBD goods can. For this reason, hemp products reman legal, while marijuana products are still controlled.
People use CBD to do a variety of things, but pain relief, anxiety management, and anti-inflammatory effects are the main reported uses.
What Is Ulcerative Colitis?
The pain associated with ulcerative colitis is like nothing else. Imagine looking healthy on the outside but feeling immense pressure from within, as if your insides are being ripped out through a wound that won’t stop bleeding no matter how hard you try to slow it down.

It’s not just about having an attack either; for some patients, entire lives will be full of flare-ups. In between these episodes, they’ll be in what’s called remission. But even then, the fear of symptoms returning can be all-consuming.
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is an inflammatory bowel disease that manifests as long-term irritation and ulcers (sores) in the lining of the colon and rectum. Ulcerative colitis can occur at any age, but it often starts during young adulthood or adolescence.
Related: CBD for Back Pain Relief
The exact cause of ulcerative colitis is unknown, but it’s thought to be a combination of environmental factors and an abnormal response by the body’s immune system. There are several different types of ulcerative colitis, depending on which part of the colon is affected.
The most common type is ulcerative proctitis, which involves only the rectum. However, pan-enteritis involves the entire colon.
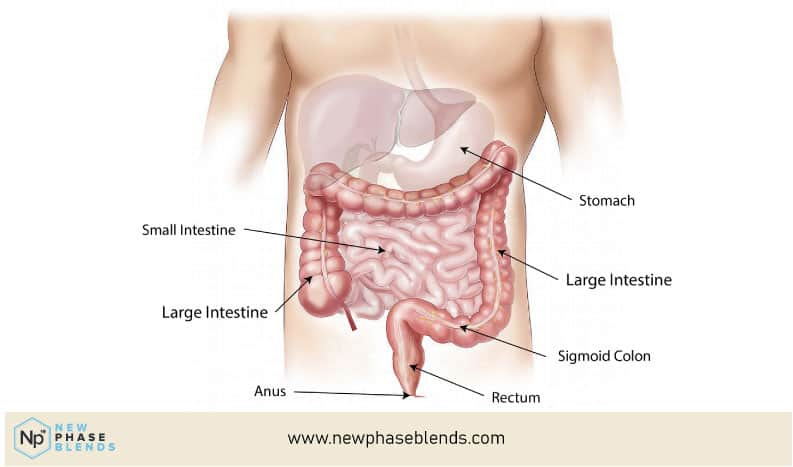
Left-sided colitis affects the rectum and sigmoid colon (the left-hand side of the descending colon). Pancolitis involves the entire colon. Fulminant colitis is a severe form of pancolitis. If you have this, you will need to go to the hospital right away.
Ulcerative colitis can be painful and debilitating and sometimes leads to life-threatening complications. Unfortunately, there is no cure for UC, but there are treatments that can help.
Discover: The Best CBD Gummies for Pain
Symptoms and Causes of Ulcerative Colitis
While researchers don’t fully understand the cause of inflammatory bowel diseases such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease, they suspect that hereditary factors are significant players in their development.
These autoimmune conditions involve a person’s immune system attacking healthy cells instead of its “intruders,” which causes chronic intestinal inflammation throughout your body–inside your gut! But why do our bodies do something so harmful?
Unfortunately, that question still has yet to be answered.
Ulcerative colitis symptoms include:
- Bloody stool
- Abdominal pain
- Cramping
- Low energy and fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Loose and frequent bowel movements
- Persistent diarrhea
However, these problems are not long-lasting; a person with ulcerative colitis may go months without experiencing any symptoms before being hit by severe flare-ups again from time to time.
Traditional Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis
In theory, Ulcerative colitis is considered incurable, although various medicines may be used to manage abdominal discomfort and reduce inflammation. Aminosalicylates are the most common IBD therapy, but a doctor might also give antibiotics or cortisone.
Ulcerative colitis can lead to strictures, which are long narrow bands of tissue that form in the large intestine due to damage or inflammatory response. Surgery may be required in more severe circumstances to remove the most diseased segment of the colon.
The illness might sometimes be cured with surgical removal of the colon, but it may severely disrupt a person’s life and cause them to need a colostomy bag to poop in.
Treating Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a condition that causes inflammation in the digestive tract. The two most common types of IBD are Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. There is no cure for IBD, but there are treatments that can help to reduce symptoms and improve quality of life.
Currently, the most effective treatments for treating IBD are clinical trials of medical cannabis. Cannabis has been shown to be effective in reducing inflammation in the digestive tract, which can lead to a reduction in symptoms.

In addition, medical cannabis can also help to improve appetite, reduce weight loss, and increase the absorption of nutrients. Medical cannabis may become an essential treatment for inflammatory bowel disease with continued research.
CBD as an Alternative Treatment for Ulcerative Colitis
CBD has shown promise as an ulcerative colitis treatment. Cannabidiol, or CBD, is one of many active chemicals found in the cannabis plant. CBD (cannabidiol) is devoid of the psychotropic effects associated with THC (tetrahydrocannabinol).
This implies that it does not result in the “high” felt after marijuana use.
CBD has analgesic (pain-relieving) and anti-inflammatory properties. These properties make CBD an attractive treatment option for ulcerative colitis. A 2017 study found that CBD effectively reduced inflammation in rats with colitis.
A 2018 review of studies concluded that CBD might be a promising treatment for inflammatory bowel diseases, including ulcerative colitis. However, more research is needed to confirm these findings. CBD is available in many different forms, including oils, capsules, and creams. It can be taken orally or applied topically to the skin. CBD is also available in marijuana (cannabis) strains that can be smoked or vaporized.

CBD is generally considered safe. However, it can cause side effects, such as diarrhea, fatigue, and changes in appetite. It can also interact with certain medications. Therefore, talking to your doctor before taking CBD if you have UC or other health conditions is essential.
Research on CBD for Ulcerative Colitis
Even though clinical trials are still lacking, many specific scientific investigations have been carried out on the effects of CBD on ulcerative colitis. For example, one study found that CBD effectively reduced inflammation and promoted healing in rats with colitis.
Another study looked at the use of CBD in human patients and found that it was well tolerated and may help treat colitis symptoms. While more research is needed to confirm these results, it is clear that CBD shows promise as a potential treatment for this condition.

Cannabinoid treatment for UC is still in its early stages. Therefore, much study is required to assess CBD oil’s effectiveness for individuals with UC. However, there is some evidence that CBD oil can be beneficial, although there is no information about dosage or administration route at this time.
CBD has been shown in some studies to help relieve Crohn’s disease symptoms. Furthermore, CBD might assist those suffering from the condition by providing more symptomatic relief and helping improve the quality of life. However, it is critical to remember that you should continue to take all of your prescribed medicines if you have UC.
Related: Taking CBD for Muscle Pain
If you’re considering stopping taking your medications or adding CBD to your treatment plan, speak with your doctor first. If you decide to try CBD, several high-quality CBD oil manufacturers are currently selling legal products in all 50 states of the United States.
However, we advise that everyone conduct their own research (or speak with their physician) to find which product will work best for them.
Randomized Controlled Trial on Cannabis Oil
Randomized controlled trials are the gold standard for clinical research, and they are essential for determining whether a new treatment is effective. In a recent trial, the effects of medical marijuana on patients with IBD symptoms were compared to those of a placebo group.
A clinical trial is essential for determining whether a new treatment is effective. In a recent trial, the effects of medical marijuana on patients with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) were compared to those of a placebo group. The results showed that patients in the cannabis group compared had significantly lower levels of UC symptoms than those in the placebo group.

This is a promising finding, as it suggests that medical marijuana may be an effective treatment for IBD. However, more extensive and more definitive trials are needed to confirm these results.
CBD Oil for Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis
It’s critical to pick a form of CBD that is most helpful for your condition if you decide to utilize it for ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease. CBD can be found in oil drops, capsules, edibles, vapes, and topical products; each has its bioavailability, targets different ailments, and is intended for various modes of administration.
CBD oil is one of the most popular forms of CBD because it is nearly always well-tolerated, easy to take, and provides relief for a wide variety of symptoms and conditions. CBD oil can be taken orally using a sublingual CBD tincture (dropper) placed under the tongue, or it can be added to food or drinks. In addition, CBD can be applied topically to the skin in the form of a lotion, oil, cream, or balm.
Capsules and edibles are also popular forms of CBD. Capsules are easy to take and provide relief for an extended period, while edibles offer a tasty way to consume CBD. However, it is essential to remember that edibles can take a long time to take effect (up to two hours), so they are not the best choice if you need immediate relief.
Vapes and topical products are less commonly used forms of CBD, but they can be very effective. Vaping CBD provides the fastest relief of any method, but it is not suitable for everyone. Topical products are best used to target specific body areas, such as inflamed joints or muscles.
Choosing the Right CBD Spectrum for Ulcerative Colitis
The first thing you need to know about CBD oil is that there are three different types, or ‘spectrums.’
The full spectrum CBD oil variety contains all of the chemical compounds found in cannabis plants, including other substances like terpenes and flavonoids, giving them their distinctive aroma or coloration abilities, respectively – but no THC! It’s important for people who want a relaxing psychoactive high without mind-altering effects on moods because it doesn’t make users feel “high.”

The second form of CBD oil, known as broad-spectrum, includes all phytocannabinoids extracted from cannabis, except for THC. This variety makes it ideal for those who do not want a psychoactive high but still appreciate some medical benefits associated with marijuana, such as pain relief and mood enhancement!
The third type of oil is known as isolate, which contains pure cannabidiol. Users who are allergic to specific cannabinoids, or want access to only the medicinal properties without any intoxicating effects, can opt for this option -CBD Isolate.
CBD Oil Dosage for Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease
The dosage of CBD oil you need will depend on several factors, including your weight, the severity of your symptoms, and the type of product you are using. Start with a low dose and increase gradually until you find the amount that works best for you.
- Capsules and edibles: start with a low dose (10-20mg) and increase gradually.
- Tinctures: start with one drop (0.5-1mg), increase as needed
- Vapes: start with one puff (0.5-1mg), increase as needed
- Topicals: apply as needed
It is important to remember that CBD is not a cure for ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease. These conditions are chronic and currently have no known cure. However, CBD might be able to provide relief from symptoms and help you manage your condition. Speak with your doctor if you consider adding CBD to your treatment plan.
CBD is a promising treatment option for UC and Crohn’s disease, but more research is needed to assess its effectiveness. CBD is generally well-tolerated, but it can cause side effects, so start with a low dose and gradually increase as needed. If you consider adding CBD to your treatment plan, speak with your doctor first.
CBD Products for Sale
Finding legitimate CBD products for sale can be overwhelming, but it is essential to know what questions you need to answer before purchasing with so many options. Avoid products that make promises about being able to cure something or say they’re the only brand worth trying out because these statements aren’t always factual in all cases!

If taking other medications while using CBD consult your healthcare provider beforehand; just as much care needs to go into selecting vendors who sell high-quality goods at competitive prices.
Summary
It’s no secret that recreational marijuana is becoming more and more popular. And while many people still associate pot with laziness or listlessness, the truth is that cannabis can have a range of positive effects on your health that don’t come along with those side effects. This is especially true for people who suffer from inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), such as ulcerative colitis.
CBD, or cannabidiol, is one of the active ingredients in marijuana, and recent studies have shown that it can effectively treat IBD symptoms. Therefore, CBD is an appealing option for people looking for symptom relief without the risks associated with marijuana. If you are considering using CBD to treat your IBD, be sure to consult with your doctor first to ensure that it is the right choice for you.
References
Patient Info: https://patient.info/digestive-health/inflammatory-bowel-disease/aminosalicylates











